5G
Evolution of 1g to 5g
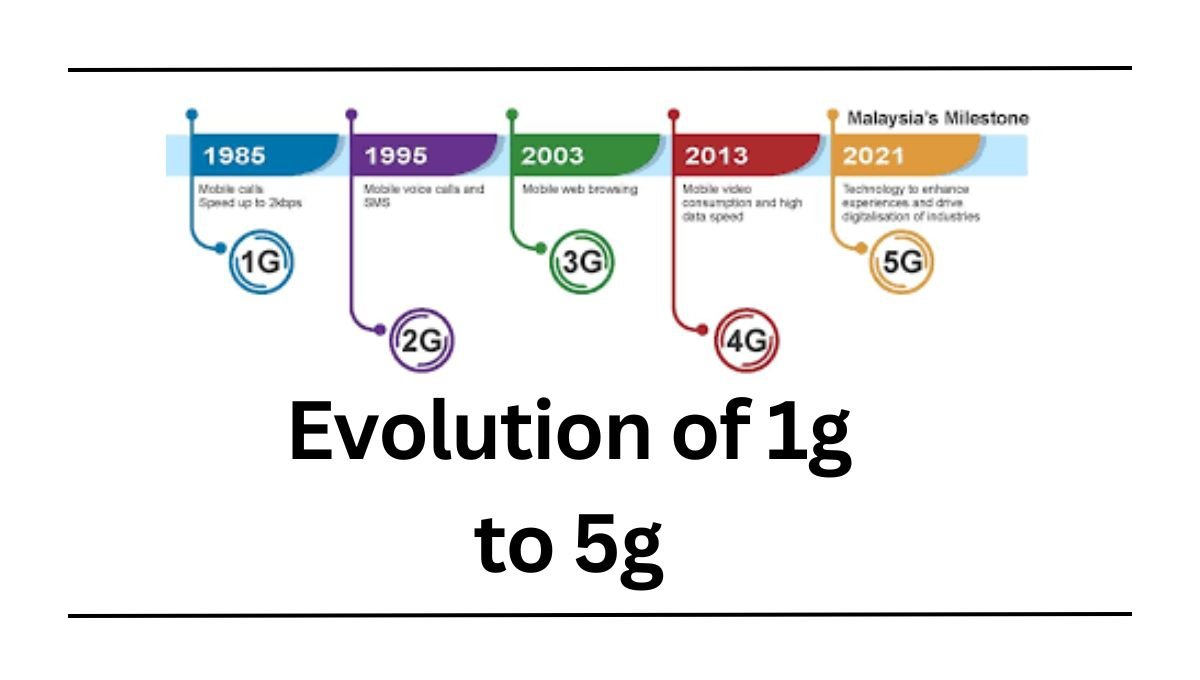
From Analog Calls to Immersive Experiences: The Evolution of Mobile Networks from 1G to 5G
The way we connect has undergone a radical transformation in the past few decades. From bulky brick phones making scratchy calls to sleek devices streaming high-definition videos, the journey from 1G to 5G has been remarkable. This article delves into the evolution of mobile networks, highlighting the key features and impacts of each generation.
Highlighting the key features and impacts of each generation.
1G: The Dawn of Cellular (1979–1991)
- Technology: Analog
- Speed: 2.4 kbps
- Applications: Voice calls only
The first-generation (1G) networks were like the primordial soup of mobile communication. They offered basic voice calls with limited coverage and poor quality. Imagine crackling calls with frequent drops—a far cry from today’s crystal-clear conversations.
2G: Stepping into the Digital Age (1991–2000)
- Technology: Digital (GSM, CDMA)
- Speed: Up to 64 kbps
- Applications: Voice calls, SMS, basic data services
2G ushered in the digital era, replacing analog signals with cleaner and more efficient digital transmission. This paved the way for Short Message Service (SMS), allowing text-based communication. While data speeds were still modest, they enabled rudimentary internet access and email on mobile devices.
3G: Unleashing the Mobile Internet (2000–2010)
- Technology: WCDMA, CDMA2000
- Speed: Up to 2 Mbps
- Applications: Mobile internet, video calls, multimedia messaging
The arrival of 3G marked a significant leap forward. With significantly faster data speeds, users could finally experience a true mobile internet. Video calls, music streaming, and basic mobile apps became a reality, transforming how we consumed information and interacted on the go.
4G: The Era of Smartphones and Social Media (2010–present)
- Technology: LTE, LTE-Advanced
- Speed: Up to 100 Mbps
- Applications: High-speed internet, video streaming, gaming, social media
4G brought about the explosive growth of smartphones and social media. With blazing-fast internet speeds, users could stream high-definition videos, play online games, and engage in real-time social interactions. From ride-hailing apps to video conferencing, 4G fueled the mobile revolution, shaping how we live, work, and connect.
5G: The Future Unfolds (2020–present)
- Technology: New Radio (NR)
- Speed: Up to 20 Gbps (theoretical)
- Applications: Internet of Things (IoT), autonomous vehicles, virtual reality, augmented reality
5G is still in its early stages, but it promises to be a game-changer. With incredibly high speeds, ultra-low latency, and massive network capacity, 5G will unlock a new era of possibilities. Imagine connecting billions of devices seamlessly, enabling smart cities, autonomous vehicles, and immersive virtual and augmented reality experiences.
Comparison of 1G to 5G technology

Conclusion:
The evolution of mobile networks from 1G to 5G is a testament to human ingenuity and the relentless pursuit of progress. Each generation has brought significant improvements in speed, reliability, and capabilities, fundamentally changing how we communicate and interact with the world around us. As we step into the 5G era, we can only imagine the exciting applications and experiences that lie ahead. The future of mobile technology is bright, and it’s all thanks to the remarkable journey from simple analog calls to the immersive possibilities of 5G.
FAQs
Is 5G available worldwide?
While 5G deployment is ongoing globally, its availability varies by region. Developed urban areas typically experience faster adoption than rural or remote locations.
How does 5G impact battery life on mobile devices?
5G can be more power-intensive than previous generations, potentially affecting battery life. However, advancements in device optimization aim to mitigate these concerns.
What are the potential health effects of 5G radiation?
Extensive research is ongoing, but current evidence suggests that 5G radiation levels are within safe limits defined by regulatory bodies.
Can existing devices be upgraded to support 5G?
In most cases, devices need specific hardware to support 5G. While some newer models are 5G-ready, older devices may not be upgradeable.
How will 5G impact rural areas with limited connectivity?
Bridging the digital divide is a challenge, but initiatives are underway to extend 5G coverage to rural and underserved areas, promoting inclusive connectivity.
5G
5G vs 4G: What’s the Real Difference?
Introduction
The transition from one generation to the next in the realm of mobile communication frequently seems like a leap into the future. But what exactly makes 5G stand apart from 4G? While 4G revolutionized mobile communication by making high-speed internet a standard, 5G promises to take connectivity to a whole new level.
In this article, we’ll break down the differences between 4G and 5G, exploring their unique features, benefits, and challenges. Let’s dive in!
Understanding 4G Technology
Evolution of 4G
4G, or the fourth generation of mobile networks, debuted in the late 2000s. It was a game-changer, introducing high-speed internet capable of supporting video streaming, online gaming, and advanced mobile applications.
Key Features of 4G
- Speed: With speeds up to 100 Mbps, 4G networks made it easy to browse, download, and stream seamlessly.
- Latency: Latency in 4G is around 50 milliseconds, which is sufficient for most real-time applications.
- Connectivity: 4G networks significantly improved data transfer and call quality compared to 3G.
Introduction to 5G Technology
What is 5G?
5G is the fifth generation of mobile networks, promising blazing-fast speeds, ultra-low latency, and the ability to connect a massive number of devices simultaneously. Launched globally in the late 2010s, 5G is designed to support emerging technologies like IoT, augmented reality (AR), and autonomous vehicles.
Core Features of 5G
- Enhanced Speed: Speeds can reach up to 10 Gbps, making it up to 100 times faster than 4G.
- Ultra-Low Latency: With latency as low as 1 millisecond, 5G enables near-instantaneous communication.
- Massive Connectivity: 5G can support up to 1 million devices per square kilometer, a critical improvement for IoT and smart cities.
Key Differences Between 4G and 5G
Speed Comparison
While 4G offers respectable speeds, 5G delivers a dramatic increase, enabling seamless 4K video streaming and large file transfers in seconds.
Latency Differences
Latency in 5G is almost negligible, making it ideal for applications like remote surgery and real-time gaming, where every millisecond counts.
Network Capacity
5G’s ability to handle a high density of devices ensures better performance in crowded areas, like stadiums or concerts.
Coverage Area and Deployment
4G networks currently cover a broader area than 5G, but as 5G infrastructure expands, it’s expected to catch up.
4g vs 5g comparison table
| Feature | 4G | 5G |
|---|
| Launch Year | 2009-2010 | 2019-2020 |
| Peak Speed | Up to 1 Gbps | Up to 10 Gbps |
| Latency | 20-50 milliseconds | 1-10 milliseconds |
| Bandwidth | Lower bandwidth compared to 5G | Significantly higher bandwidth |
| Frequency Bands | 700 MHz to 2.6 GHz | 24 GHz to 100 GHz |
| Capacity | Limited devices per network cell | Supports a higher density of devices |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderately energy efficient | More energy-efficient per data unit |
| Use Cases | Mobile internet, streaming, video calls | IoT, smart cities, autonomous vehicles, AR/VR |
| Coverage | Wider coverage globally | Limited initially, expanding gradually |
| Technology | LTE (Long-Term Evolution) | mmWave, Sub-6 GHz, Massive MIMO |
| Connection Density | Up to 100,000 devices per square kilometer | Up to 1 million devices per square kilometer |
| Deployment Cost | Lower relative cost | Higher infrastructure cost initially |
| Primary Benefits | Faster internet speeds than 3G | Ultra-low latency, high speeds, and reliability |
| Drawbacks | Struggles with high congestion areas | Requires dense infrastructure (small cells) |
Benefits of 5G Over 4G
Advantages in Daily Life
- Streaming and Gaming: Experience buffer-free streaming and lag-free gaming, even in high resolutions.
- IoT Integration: From smart homes to wearable tech, 5G enhances the functionality of connected devices.
Business and Industrial Impacts
- Smart Cities: 5G facilitates real-time data sharing, powering innovations like traffic management and public safety systems.
- Automation and Robotics: Industries can achieve greater efficiency with 5G-enabled automation and robotics.
Challenges of 5G Technology
Infrastructure Demands
Deploying 5G requires building new towers and upgrading existing infrastructure, which is both time-consuming and expensive.
Device Compatibility
Not all devices support 5G, necessitating upgrades for consumers and businesses alike.
Cost of Deployment
The transition to 5G involves significant costs for telecom companies, which could impact pricing for end users.
How 4G Still Holds Relevance
Existing Infrastructure
4G networks are well-established, ensuring reliable connectivity in areas where 5G is not yet available.
Accessibility and Affordability
For users who don’t require the advanced features of 5G, 4G remains a cost-effective and efficient option.
The Future of Connectivity
5G’s Potential to Revolutionize Communication
With its unparalleled speed and connectivity, 5G is paving the way for technological advancements we can only imagine today.
What Lies Beyond 5G?
Research into 6G and beyond suggests even more transformative possibilities, including holographic communication and brain-computer interfaces.
Conclusion OF 5G vs 4G
Both 4G and 5G have their unique strengths and challenges. While 4G continues to serve as a reliable and affordable option for many, 5G is undoubtedly the future of connectivity. As the technology matures, it will unlock opportunities we’ve yet to fully grasp.
FAQs
1. What is the primary difference between 4G and 5G?
The primary difference is speed and latency—5G offers faster speeds and significantly lower latency than 4G.
2. Can 5G completely replace 4G?
Not yet. 5G is still being deployed, and 4G remains essential in areas without 5G coverage.
3. Do I need a new phone for 5G?
Yes, a 5G-compatible phone is required to access 5G networks.
4. How does 5G impact battery life?
5G can consume more battery, but modern devices are optimized to handle the increased demand efficiently.
5. Is 5G available everywhere?
No, 5G coverage is still expanding and is not yet available in many rural or remote areas.
5G
How 5G technology works
Introduction
Ever wondered why everyone is so hyped about 5G? It’s not just another generation of mobile networks—it’s a game-changer! 5G technology promises lightning-fast speeds, near-instant connectivity, and the power to revolutionize everything from smart cities to healthcare. Let’s dive into how this amazing technology works and what makes it so unique.
From 1G to 4G: A Quick Recap
To understand 5G, let’s rewind a bit.
- 1G: The era of analog voice calls.
- 2G: introduced digital voice and text messaging.
- 3G: Brought mobile internet to life.
- 4G: Revolutionized streaming with faster internet speeds.
Each generation was a leap forward, but even 4G has its limitations.
Key Limitations of 4G
- Speed: Struggles with handling high traffic in dense areas.
- Latency: Not fast enough for real-time applications like autonomous vehicles.
What Makes 5G Different?
Defining Characteristics of 5G
5G isn’t just faster—it’s smarter and more efficient.
- Speeds up to 100 times faster than 4G.
- Ultra-low latency, meaning minimal delay in data transmission.
- Capacity to connect millions of devices simultaneously.
Speed and Latency Improvements
With 5G, downloading a movie takes seconds, and online gaming feels like a face-to-face duel with zero lag. Impressive, right?
Massive Device Connectivity
From smart homes to wearable devices, 5G enables a network where everything is interconnected.
How Does 5G Technology Work?
How 5G technology works
Key Components of 5G Infrastructure
Small Cells
Tiny base stations scattered throughout cities provide uninterrupted coverage.
Massive MIMO (Multiple Input, Multiple Output)
Think of it as a multi-lane highway for data—more lanes mean more traffic handled efficiently.
Beamforming
Directs signals precisely to devices, avoiding interference.
Spectrum Bands Used in 5G
Low Band
Great for wide coverage but offers moderate speeds.
Mid Band
Balances speed and coverage, ideal for cities.
High Band (mmWave)
Blazing fast speeds but limited range—perfect for hotspots.
The Role of Network Slicing in 5G
What is Network slicing?
Network slicing allows one 5G network to act as multiple virtual networks, tailored for different needs.
Benefits of Network Slicing for Businesses
- Prioritized data for critical applications.
- Customizable bandwidth allocation.
Real-World Applications of 5G
IoT: The Internet of Things, Powered by 5G
5G’s ability to connect a massive number of devices simultaneously, combined with its low latency and high reliability, makes it the ideal technology for powering the Internet of Things (IoT).
Potential Applications of IoT with 5G:
- Smart Cities: 5G can enable the development of smart cities by connecting various devices and sensors, such as traffic lights, smart streetlights, and environmental sensors. This can lead to improved traffic management, energy efficiency, and public safety.
- Smart Homes: 5G can power smart homes by connecting devices like smart thermostats, security cameras, and voice assistants. This can enhance home automation, energy efficiency, and security.
- Industrial IoT: 5G can revolutionize industries by enabling the connection of machines, sensors, and robots. This can lead to increased productivity, efficiency, and safety in manufacturing, logistics, and other sectors.
Autonomous Vehicles: The Future of Transportation
Autonomous vehicles require reliable, low-latency communication to make real-time decisions and coordinate with other vehicles and infrastructure. 5G’s low latency and high reliability make it the ideal technology for supporting autonomous vehicle technology.
How 5G Can Support Autonomous Vehicles:
- Vehicle-to-Vehicle (V2V) Communication: 5G enables real-time communication between vehicles, allowing them to share information about their speed, direction, and braking.
- Vehicle-to-Infrastructure (V2I) Communication: 5G allows vehicles to communicate with infrastructure, such as traffic lights and road signs, to improve traffic flow and safety.
- Remote Control of Autonomous Vehicles: 5G enables remote control of autonomous vehicles, allowing operators to intervene in case of emergencies or complex situations.
Remote Healthcare: Transforming Healthcare Delivery
5G’s high bandwidth and low latency can revolutionize healthcare delivery by enabling remote consultations, telemedicine, and remote surgery.
Potential of 5G in Remote Healthcare:
- Remote Consultations: 5G enables high-quality video conferencing, allowing doctors to consult with patients remotely.
- Telemedicine: 5G can enable remote monitoring of patients’ vital signs, allowing for early detection and intervention of health issues.
- Remote Surgery: 5G’s low latency and high reliability make it possible to perform remote surgery, allowing surgeons to operate on patients from a distance.
Challenges and Opportunities of 5G in Healthcare:
- Security and Privacy: Protecting patient data is a major concern in healthcare. Strong security measures must be implemented to ensure the confidentiality and integrity of patient information.
- Regulatory Hurdles: Regulations and standards need to be developed to ensure the safe and effective use of 5G in healthcare.
- Infrastructure Costs: Deploying 5G infrastructure in rural and underserved areas can be costly. Government and industry partnerships are needed to bridge the digital divide.
Conclusion
5G technology is poised to revolutionize the way we live, work, and communicate. With its unprecedented speeds, low latency, and massive capacity, 5G is unlocking a new era of innovation and connectivity. From powering the Internet of Things to enabling autonomous vehicles and remote healthcare, 5G’s potential is vast.
However, the full realization of 5G’s potential will depend on several factors, including the deployment of robust 5G networks, the development of new applications and services, and the adoption of advanced technologies like edge computing and artificial intelligence. As 5G continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more exciting developments in the years to come.
FAQ
What is the physics behind 5G?
Compared to its predecessor, 4G, 5G offers ten times as much capacity. Because 5G employs additional higher-frequency waves to encode and transmit data in addition to low and medium-frequency radio waves, the increased bandwidth is made possible. Bandwidth is comparable to a highway’s width.
How does 5G signal travel?
Radio frequencies, sometimes referred to as spectrum, are used by wireless communications systems to transmit data over the atmosphere. 5G functions similarly, although it makes use of higher, less congested radio frequencies. As a result, it can convey more data much more quickly.
Who has the largest 5G network in the world?
Huawei, Shentong Metro, and China Mobile Shanghai Create the Biggest 5G Private Rail Network in the World The largest 5G private rail network in the world is being built by Huawei, Shentong Metro, and China Mobile Shanghai.
Is 5G faster than LTE?
The speed and reduced latency of 5G are its primary advantages over 4G LTE. In order to provide faster speeds, lower latency, higher capacity, and more dependable broadband than 4G LTE networks, 5G networks are based on a new radio technology called 5G NR, which uses high-frequency radio waves.
5G
5g network components
5G has emerged as a game-changer, promising unprecedented speed, reliability, and connectivity. As we delve into the intricacies of 5G network components, it becomes evident that this revolutionary technology is not merely an upgrade but a paradigm shift. Let’s unravel the key components shaping the future of connectivity.
Introduction to 5G Network Components
The journey into the world of 5G begins with an understanding of its core components. Unlike its predecessors, 5G is not just about faster internet on your smartphone; it’s a holistic transformation of the entire network infrastructure.
The Core Elements of 5G Networks
1. Millimeter Waves
One of the pillars of 5G is the utilization of millimeter waves, enabling higher data transfer rates. These waves, operating in the 30-300 GHz range, pave the way for faster and more efficient communication.
2. Small Cells
In contrast to traditional large-cell towers, 5G relies on a dense network of small cells. These compact stations enhance coverage and capacity, ensuring a seamless user experience in densely populated areas.
3. Massive MIMO
Massive Multiple Input, Multiple Output (MIMO) technology plays a crucial role in 5G networks. By using numerous antennas, massive MIMO optimizes data transfer, minimizing latency, and boosting network efficiency.
Radio Access Network (RAN) in 5G
1. Base Stations
At the heart of 5G’s RAN are base stations, connecting devices to the network. These stations facilitate the exchange of data, ensuring a reliable and high-speed connection.
2. Antennas
The deployment of advanced antennas is a key component in achieving the high speeds promised by 5G. These antennas come in various forms, each catering to specific needs and scenarios.
3. Backhaul
Efficient backhaul mechanisms ensure the seamless flow of data between the core network and the RAN. The backhaul is a critical aspect of 5G infrastructure, contributing to low latency and high bandwidth.
Core Network Components
1. Cloud-native Architecture
5G embraces a cloud-native architecture, decentralizing network functions. This approach enhances flexibility, scalability, and resource utilization.
2. Network Slicing
Network slicing allows the creation of multiple virtual networks within the same physical infrastructure. This innovation enables tailored solutions for diverse applications, from autonomous vehicles to augmented reality.
3. Edge Computing
The integration of edge computing in 5G networks brings computing resources closer to end-users. This reduces latency and enhances the overall performance of applications and services.
Devices and User Equipment
1. 5G Smartphones
The widespread adoption of 5G smartphones is a driving force behind the network’s growth. These devices support higher data speeds, enabling users to experience the full potential of 5G connectivity.
2. IoT Devices
The Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem thrives on 5G connectivity. From smart homes to industrial sensors, 5G enables a massive influx of connected devices, transforming how we interact with our surroundings.
3. Wearables
Wearable devices, equipped with 5G capabilities, redefine the user experience. From health monitoring to augmented reality glasses, wearables leverage 5G to offer seamless and immersive functionalities.
5G Security Measures
1. Encryption
Ensuring the security of data transmission is paramount in 5G networks. Robust encryption mechanisms safeguard sensitive information, protecting users from potential cyber threats.
2. Authentication
Identity verification is a crucial aspect of 5G security. Robust authentication protocols prevent unauthorized access and ensure the integrity of the network.
3. Network Slicing Security
As network slicing becomes integral to 5G, addressing security concerns specific to each virtual network becomes imperative. Customized security measures for individual slices fortify the overall network.
Challenges and Future Developments
1. Interference and Obstacles
Despite its potential, 5G faces challenges related to interference and obstacles. Addressing these issues is crucial for ensuring consistent and reliable connectivity.
2. Integration with Existing Networks
Integrating 5G with existing networks poses challenges. Compatibility issues need to be resolved for a smooth transition and coexistence with 4G and other technologies.
3. Anticipated Technological Advancements
The future holds promises of technological advancements in 5G, including improved efficiency, higher data rates, and novel applications. Staying ahead of the technological curve is essential for harnessing the full potential of 5G.
The Impact of 5G Network Components
1. Enhanced Connectivity
5G’s impact extends beyond speed; it revolutionizes connectivity. From faster downloads to real-time communication, 5G sets the stage for a connected future.
2. Transformative Industries
Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, and transportation undergo transformative changes with the integration of 5G. Enhanced efficiency and communication redefine traditional processes.
3. Advancements in Healthcare
The healthcare sector witnesses groundbreaking advancements with 5G, from remote surgeries to real-time patient monitoring. The reliability of 5G connectivity plays a pivotal role in these innovations.
Comparisons with Previous Generations
1. Speed and Latency
Comparing 5G with its predecessors reveals unparalleled speed and reduced latency. The difference is not just incremental; it’s a leap into a new era of instantaneous communication.
2. Network Capacity
The increased network capacity of 5G enables the simultaneous connection of a massive number of devices. This scalability is a significant leap forward from previous generations.
3. Use Cases
From smart cities to smart agriculture, 5G’s use cases surpass the boundaries of traditional networking. Exploring these diverse applications reveals the versatility of 5G technology.
The Global Rollout of 5G
1. Leading Countries in 5G Adoption
Certain countries lead the global race in adopting 5G technology. Understanding the trends in these nations provides insights into the global evolution of 5G.
2. Economic Implications
The economic impact of 5G is profound, influencing industries, job markets, and innovation. Nations investing in 5G have witnessed a surge in economic growth and technological advancements.
3. Regulatory Frameworks
The development and implementation of robust regulatory frameworks are essential for the successful deployment of 5G. Balancing innovation with ethical and safety considerations is a delicate task.
Future Applications and Possibilities
1. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR)
The combination of 5G and AR/VR opens up new dimensions of immersive experiences. From gaming to professional training, the possibilities are limitless.
2. Autonomous Vehicles
5G plays a pivotal role in the evolution of autonomous vehicles. Real-time communication and data exchange are critical for ensuring the safety and efficiency of self-driving cars.
3. Smart Cities
The concept of smart cities is not a distant dream but a tangible reality with 5G. From intelligent traffic management to energy-efficient solutions, 5G transforms urban living.
Addressing Concerns and Misconceptions
1. Health Concerns
Public concerns regarding the health implications of 5G require transparent communication. Addressing these concerns with scientific facts is crucial for fostering public trust.
2. Environmental Impact
Examining the environmental impact of 5G infrastructure is essential. Balancing technological progress with eco-friendly practices ensures a sustainable future.
3. Privacy Issues
As 5G facilitates a hyper-connected world, privacy concerns come to the forefront. Striking a balance between connectivity and individual privacy is an ongoing challenge.
The Role of 5G in Industry 4.0
1. Smart Manufacturing
In the era of Industry 4.0, 5G plays a pivotal role in smart manufacturing. From predictive maintenance to efficient supply chain management, 5G transforms the manufacturing landscape.
2. Supply Chain Optimization
Efficient supply chain management becomes a reality with 5G. Real-time tracking, data analytics, and automation enhance the overall efficiency of supply chain operations.
3. Industrial IoT
The integration of 5G with the Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) ushers in a new era of connectivity and control. Industrial processes become more agile, responsive, and intelligent.
Tips for Harnessing the Power of 5G
1. Business Integration
Businesses can leverage 5G by integrating it into their operations. From improved customer experiences to enhanced efficiency, the benefits are vast.
2. User Education
Educating users about the capabilities and implications of 5G is essential. Empowered users make informed choices, contributing to the responsible and widespread adoption of 5G.
3. Collaborative Innovation
The true potential of 5G unfolds when industries collaborate on innovative solutions. Cross-sector collaborations drive advancements and open up new possibilities for 5G applications.
Conclusion
In conclusion, 5G network components represent the cornerstone of the digital future. From millimeter waves to advanced security measures, each element contributes to the unparalleled connectivity and transformative potential of 5G. Embracing this technology requires addressing challenges, fostering innovation, and navigating ethical considerations. As we stand on the brink of a connected era, the impact of 5G extends beyond faster downloads—it reshapes industries, societies, and daily experiences.
FAQs About 5G Network Components
Is 5G safe for health?
Addressing common concerns about the potential health impact of 5G.
How does 5G differ from previous generations?
Exploring the key differences in speed, latency, and network capacity.
What industries benefit the most from 5G?
Highlighting the transformative impact of 5G on various industries.
How can businesses integrate 5G effectively?
Providing practical tips for businesses to harness the power of 5G.
What are the future possibilities of 5G technology?
Delving into the potential applications and advancements in the 5G landscape.

 5G2 years ago
5G2 years agoHow 5G Technology Will Revolutionize Our Lives and Work

 Tech5 months ago
Tech5 months ago3d Printer Technology (Application) (History) And (Types)

 5G2 months ago
5G2 months agoWhat is the difference between 5G and 5G Plus?

 Computer1 year ago
Computer1 year ago“Bleeping Computer: Your Ultimate Guide to Cybersecurity”

 5G1 year ago
5G1 year agoDifference between 5G nsa and 5G sa

 5G1 year ago
5G1 year agoHow does 5g work on iPhone?

 5G1 year ago
5G1 year agoThe Future of 5G Technology : Revolutionizing Connectivity

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoExplain How Technology Has Affected People’s Activity Levels








